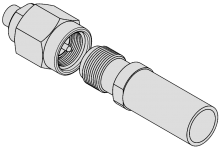
This coupling mechanism consists of a basic thread and nut design. Screw-on connections are the most commonly found amongst RF connector series due to their mechanical durability, however close attention must be paid to ensure coupling is not over-torqued.
Connector series featuring this mechanism include: 7/16 DIN, FME, HN, LC, LT, N, SC, SMA, SMC, TNC, and more.